开源 Python 和命令行程序 gget 可以高效、轻松地以编程方式访问存储在各种大型公共基因组参考数据库中的信息。 gget 与可获取用户生成的测序数据的现有工具一起使用 ,以取代在基因组数据分析过程中效率低下、可能容易出错的手动网络查询。虽然 gget 模块的灵感来自于繁琐的单细胞 RNA-seq 数据分析任务),但我们预计它们可用于广泛的生物信息学任务。
 gget文章
gget文章
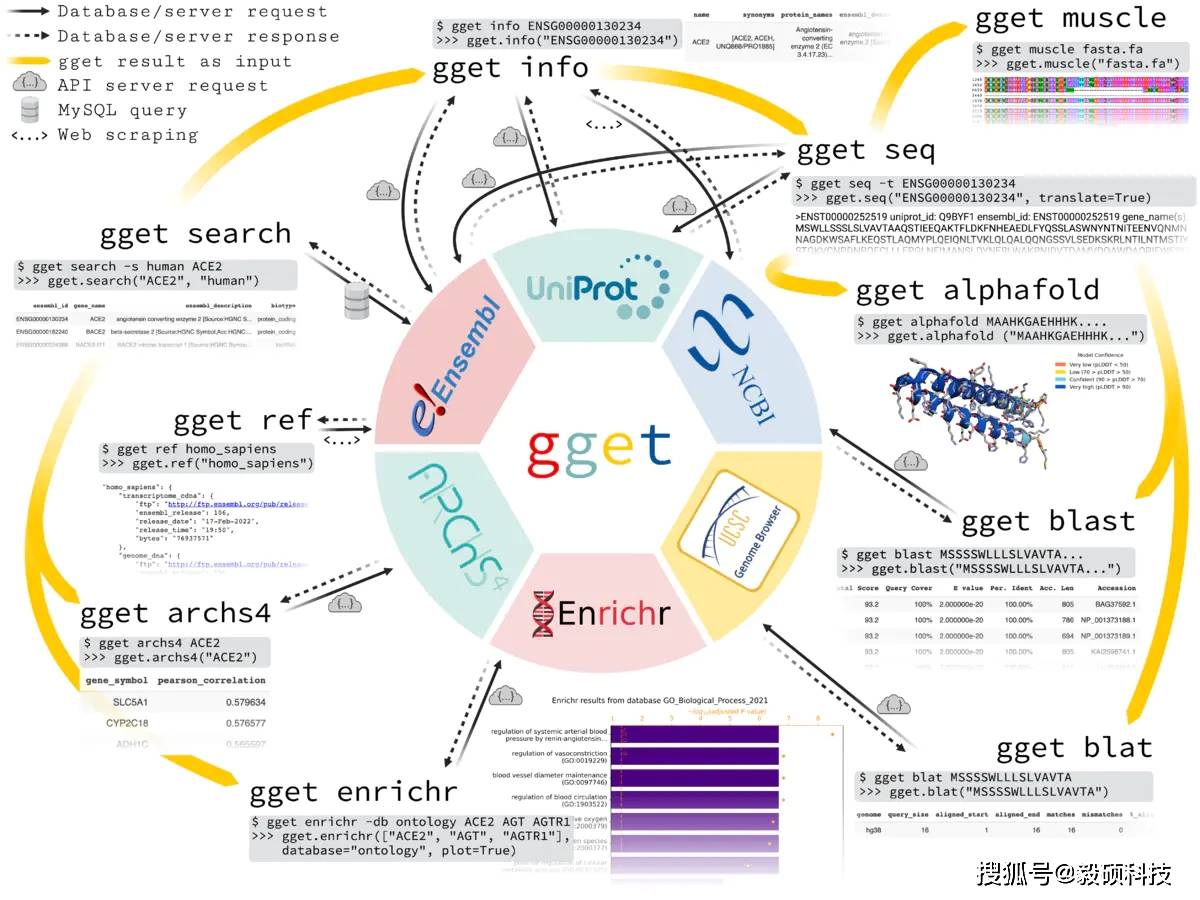
可以通过运行“pip install gget”从命令行安装 gget。下图描述了每个 gget 工具的一个用例和相应的输出。每个 gget 工具都有一个详尽的手册,可作为 Python 环境中的函数文档或在命令行中使用帮助标志 [-h] 作为标准输出。
gget overview 编辑
gget开源地址
gget地址:https://pachterlab.github.io/gget/
gget 示例存储库:https://github.com/pachterlab/gget_examples
gget安装
pip install --upgrade gget
或者
conda install -c bioconda gget
在 Jupyter Lab / Google Colab中调用
import gget
gget模块
- gget ref
Fetch File Transfer Protocols (FTPs) and metadata for reference genomes and annotations from Ensembl by species.
- gget search
Fetch genes and transcripts from Ensembl using free-form search terms.
- gget info
Fetch extensive gene and transcript metadata from Ensembl, UniProt, and NCBI using Ensembl IDs.
- gget seq
Fetch nucleotide or amino acid sequences of genes or transcripts from Ensembl or UniProt, respectively.
- gget blast
BLAST a nucleotide or amino acid sequence to any BLAST database.
- gget blat
Find the genomic location of a nucleotide or amino acid sequence using BLAT.
- gget muscle
Align multiple nucleotide or amino acid sequences to each other using Muscle5.
- gget enrichr
Perform an enrichment analysis on a list of genes using Enrichr.
- gget archs4
Find the most correlated genes to a gene of interest or find the gene's tissue expression atlas using ARCHS4.
- gget pdb
Get the structure and metadata of a protein from the RCSB Protein Data Bank.
- gget alphafold
Predict the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence using a simplified version of DeepMind’s AlphaFold2.
gget快速入门
- 命令行
# Fetch all Homo sapiens reference and annotation FTPs from the latest Ensembl release
$ gget ref homo_sapiens
# Get Ensembl IDs of human genes with "ace2" or "angiotensin converting enzyme 2" in their name/description
$ gget search -s homo_sapiens 'ace2' 'angiotensin converting enzyme 2'
# Look up gene ENSG00000130234 (ACE2) and its transcript ENST00000252519
$ gget info ENSG00000130234 ENST00000252519
# Fetch the amino acid sequence of the canonical transcript of gene ENSG00000130234
$ gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234
# Quickly find the genomic location of (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blat MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# BLAST (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blast MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Align nucleotide or amino acid sequences stored in a FASTA file
$ gget muscle path/to/file.fa
# Use Enrichr for an ontology analysis of a list of genes
$ gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1 ACE AGTRAP AGTR2 ACE3P
# Get the human tissue expression of gene ACE2
$ gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Get the protein structure (in PDB format) of ACE2 as stored in the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID returned by gget info)
$ gget pdb 1R42 -o 1R42.pdb
# Predict the protein structure of GFP from its amino acid sequence
$ gget setup alphafold # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget alphafold MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK
- Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab):
import gget
gget.ref("homo_sapiens")
gget.search(["ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"], "homo_sapiens")
gget.info(["ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"])
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True)
gget.blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.muscle("path/to/file.fa")
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"], database="ontology", plot=True)
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget.pdb("1R42", save=True)
gget.setup("alphafold") # setup only needs to be run once
gget.alphafold("MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK")
- Call gget from R using reticulate:
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
gget$ref("homo_sapiens")
gget$search(list("ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"), "homo_sapiens")
gget$info(list("ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"))
gget$seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=TRUE)
gget$blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$muscle("path/to/file.fa", out="path/to/out.afa")
gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"), database="ontology")
gget$archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget$pdb("1R42", save=TRUE)- 本文固定链接: https://maimengkong.com/moreshare/1370.html
- 转载请注明: : 萌小白 2023年1月29日 于 卖萌控的博客 发表
- 百度已收录
