常见的建树方法有:
贝叶斯法(Bayesian),最大似然法(Maximum likelihood,ML),最大简约法(Maximum parsimony,MP),邻接法(Neighbor-Joining,NJ),最小进化法(Minimum Evolution,ME),类平均法(UPGMA)。
一般来讲,如果模型合适,最大似然法的效果较好。对于近缘序列,最大简约法用的假设最少,各种方法结果相似。而对于远缘序列,一般使用最大似然法或邻接法。对相似度很低的序列,邻接法往往出现 Long-branch attraction(LBA,长枝吸引现象),严重干扰进化树的构建。对于各种方法构建分子进化树的准确性,Hall 认为贝叶斯的方法最好,其次是最大似然法,然后是最大简约法。其实如果序列的相似性较高,各种方法结果差别不大。
最大似然法和邻接法需要选择模型。对于蛋白质序列,一般选择 Poisson Correction(泊松修正)模型。而对于核酸序列,一般选择 Kimura 2-parameter(Kimura-2 参数)模型。
表 1. 构建进化树的常用软件
|
软件名称 |
简介 |
|
Clustal X |
图形化的序列比对工具 |
|
GeneDoc |
多序列比对结果美化工具 |
|
BioEdit |
序列分析综合工具 |
|
MEGA |
图形化比对,进化分析综合工具 |
|
PAUP |
进化分析工具 |
|
Phylip |
进化分析工具 |
|
PhyML |
最大似然法建树工具 |
|
PAML |
最大似然法建树工具 |
|
MrBayes |
贝叶斯法建树工具 |
|
FastTree |
最大似然法建树工具(速度快) |
|
TreeView |
进化树显示工具 |
本文主要讲 FastTree 使用方法:
首先介绍几点特性:
1. 在默认参数下,FastTree 比 PhyML 更准确,比 PhyML 快 100~1000 倍;
2. FastTree 使用模型为:核酸进化模型:Jukes-Cantor 或者 GTR(generalized time-reversible);蛋白进化模型:JTT (Jones-Taylor-Thornton 1992), WAG (Whelan & Goldman 2001) 或者 LG (Le and Gascuel 2008)
下载,安装 FastTree
FastTree 提供以下几个版本:
-
Linux 64-bit executable (+SSE)
-
Multi-threaded executable (+SSE +OpenMP) (see usage guide)
-
Windows 32-bit command-line executable (no SSE)
-
C code
下载 Windows 32-bit command-line executable (no SSE) 后,是一个 FastTree.exe 文件,可以直接在 cmd 命令行程序中调用运行。
新建一个文件夹:比如在 D 盘目录下新建一个 FastTree 文件夹,将 FastTree.exe 程序放在 D:FastTree 目录下。
FastTree 运行(Windows 为例)
-
开始菜单—搜索—cmd
-
切换目录到 D:FastTree
-
最大似然树构建:FastTree protein alignment file > tree
-
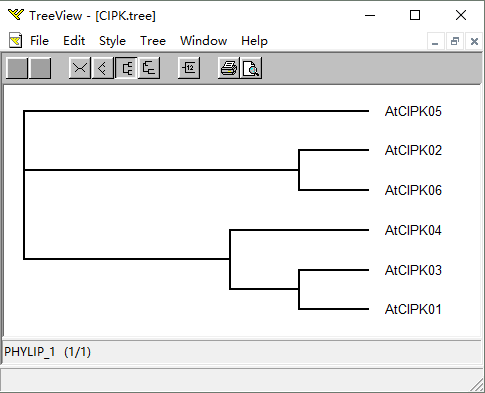
在目录 D:FastTree 生成.tree 文件,可以使用 TreeView 或 MEGA 打开。
-
构建进化树时,可以选择不同的模型:
命令行:D:FastTree>FastTree -lg CIPK.phy >CIPK.tree
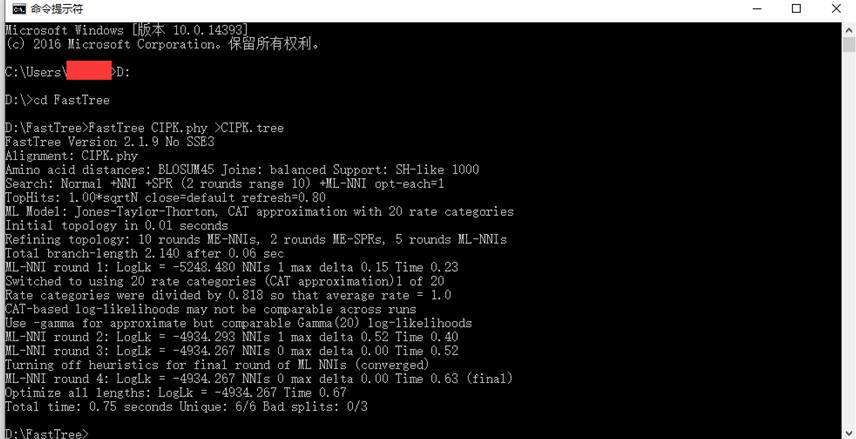
alignment file 格式

alignment file 格式如上图。
可以首先使用 Clustal X 比对序列:Alignment—Output Format Options—Phylip format
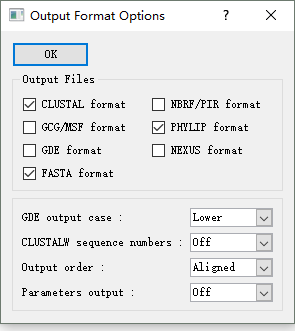
比对后,在比对目录下生成几个文件,其中.phy 后缀名文件是 FastTree 要使用的。
参考文献:
Hall B G. Comparison of the accuracies of several phylogenetic methods using protein and DNA sequences[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2005, 22(3): 792-802.
Price, M.N., Dehal, P.S., and Arkin, A.P. (2009) FastTree: Computing Large Minimum-Evolution Trees with Profiles instead of a Distance Matrix. Molecular Biology and Evolution 26:1641-1650.
Price, M.N., Dehal, P.S., and Arkin, A.P. (2010) FastTree 2 -- Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE, 5(3):e9490.
Jones D T, Taylor W R, Thornton J M. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences[J]. Computer applications in the biosciences: CABIOS, 1992, 8(3): 275-282.
Whelan S, Goldman N. A general empirical model of protein evolution derived from multiple protein families using a maximum-likelihood approach[J]. Molecular biology and evolution, 2001, 18(5): 691-699.
Le S Q, Gascuel O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix[J]. Molecular biology and evolution, 2008, 25(7): 1307-1320.
作者:muminwangzi
图片来源:muminwangzi
题图来源:丁香通
转自:丁香学术- 本文固定链接: https://maimengkong.com/kyjc/1490.html
- 转载请注明: : 萌小白 2023年4月29日 于 卖萌控的博客 发表
- 百度已收录
